Separation and divorce
You are married and you wish to separate? There are several ways to do this: you can resort to a separation (suspension of the joint household) or petition for divorce. Find out all the useful information about these two solutions and the steps to take at the Tribunal de première instance.
You wish to suspend your joint household?
Suspension of joint household allows to provisionally preserve the social and matrimonial benefits resulting from the marriage, and to officially start the 2-year period at the end of which the divorce can be requested by one spouse.
Suspending joint household life: what are the possibilities?
- You can choose to settle your separation without going to court.
- When you and your spouse agree, you can have an agreement ratified together by the Tribunal de première instance, which officially sets out the terms and consequences of the suspension of your joint household life (allocation of housing, matters relating to the minor child or children (residence and visitation rights), maintenance contribution(s), etc.).
- In the event of a conflictual separation, you can apply unilaterally to the court to request measures for the protection of the marital union. The judge will pronounce the separation by court order and will mainly settle:
- The allocation of the family home and furniture
- The allocation of residence of the minor child or children, the modalities for exercising visiting rights
- The determination of the maintenance paid to any child or children and the other spouse
How do I bring a conflict before the court?
Step 1: make your request
You should prepare your application in written form and send it to the Tribunal de première instance by mail or by dropping it off directly at the court desk or the Greffe universel, in duplicate (in triplicate if you have a minor child or children). It must be written in French and signed.
You can also use the standard form provided by the Federal Office of Justice.
Your request must include the following details:
- What you want to obtain (separation, allocation of the home, concerning the children (residence and visitation rights), maintenance contributions, etc.)
- The facts related to your request
You can act on your own, appeal to a lawyer or a legal advice service.
Step 2: Pay an advance on costs
You will be asked to pay an advance on costs. The amount may vary from 200 to 2,000 CHF, depending on the complexity of the case and the conclusions (amount of maintenance payments and other measures).
If your resources are insufficient to ensure the defence of your interests, you can request legal aid.
Step 3: attend the hearing
Usually the court will summon you to a hearing where you and your spouse appear in person.
The court then tries to bring you to an agreement. If you fail to do so, the court will make a decision on the various measures to be taken (e.g. separation, allocation of the home, matters concerning the children (residence and visiting rights), maintenance contribution(s), etc.).
The court can set the date of separation of the spouses, which will trigger the 2-year period at the end of which the spouses will be allowed to file for divorce unilaterally.
If you are in a conflict over residence or the exercise of visiting rights to your minor children, the court may decide to request a report from the parental Separation assessment and support Service (SEASP).
The court may also decide, depending on the case, to hear the minor child or children personally.
Step 4: receive the judgment
The judge's decision is communicated to you by mail, if necessary through your counsel (lawyer, legal advice service).
Do you wish to divorce?
Divorce and its consequences
Be careful, if you do not agree, the divorce cannot be pronounced before you have lived separately for 2 years (except in very exceptional cases).
What are the main effects of divorce?
- Allocation of the family home
- Determination of the maintenance contribution paid to one of the spouses
- Division of the occupational pensions' assets (2nd pillar)
- Division of the marital property between the spouses (marital property)
If you have a minor child or children, the divorce judge also resolves the following issues:
- Allocation of parental responsibility
- Allocation of residence of the minor child or children and regulation of the modalities for exercising visiting rights
- Division of the parenting credit (AVS)
- Determination of the maintenance contribution paid to the minor child or children
The joint or shared parental responsibility is the rule and the alternate residence arrangement (e.g. one week at each parent's home) is often pronounced.
The different types of divorce proceedings
There are 2 types of divorce proceedings:
- Divorce by joint request, if you both wish to divorce:
- With a comprehensive agreement, when you agree on all the effects of the divorce
- With a partial agreement, if you have agreed to divorce, but have not been able to agree on all the terms of the divorce
- Divorce at the petition of one spouse, when only one of the spouses wishes to divorce
Divorce by joint request - steps
You agree with your spouse to divorce.
Step 1: make your request
You should prepare your application in written form to the Tribunal de première instance by mail or by dropping it off at the court desk or at the Greffe universel. It must be written in French and signed by you and your spouse or by your legal counsel.
You can also use the standard form provided by the Federal Office of Justice.
Your application must be accompanied by a comprehensive agreement that sets out the effects of the divorce, including the situation of the children:
- The allocation of the family home
- The matters concerning the children (parental responsibility, residence and visiting rights)
- The maintenance contribution paid to the child or children
- The division of the parenting credit (AVS)
- The maintenance contribution paid to the spouse
- The liquidation of the marital property regime
- The division of the occupational pensions' assets (2nd pillar)
You can act on your own, appeal to a lawyer or a legal advice service.
Step 2: Pay an advance on costs (unilateral application)
You are required to pay an advance on costs of at least CHF 500.- (corresponding to half of the estimated legal costs of at least CHF 1'000.-), the amount of which varies depending on the complexity of the case and the conclusions (amount of maintenance contributions and other measures). (see art. 30 RTFMC).
Further information on the costs of a divorce proceeding
Step 3: attend the hearing
The court summons you and your spouse and hears you separately to ensure that you have filed your petition and entered into your agreement thoughtfully and willingly.
The court may also ask you about the content of your agreement, especially for points that concern the children.
If there are no more contentious issues, the court will grant the divorce and ratify the agreement on the effects of the divorce.
Step 4: receive the judgment
The judge's decision is communicated to you by mail, if necessary, through your counsel (lawyer, legal advice service).
Divorce at the petition of one spouse – steps
You want to divorce, but your spouse is refusing to do so.
You can file for divorce on a unilateral basis, especially if:
- You have lived 2 years apart at the time of filing your claim
Step 1: make your request
You should prepare your application in written form and send it to the Tribunal de première instance by mail or by dropping it off directly at the court desk or the Greffe universel, in duplicate (in triplicate if you have a minor child or children). It must be written in French and signed.
Your request must include the following details:
- What you want to obtain (divorce, allocation of the home, matters concerning the children, maintenance contributions paid to the minor child or children as well as to you, division of the parenting credit (AVS), liquidation of the marital property regime, division of the occupational pensions' assets (2nd pillar))
- The facts related to your request, by providing as much supporting documentation as possible to substantiate them.
Step 2: to pay an advance on costs
You have to pay an advance on costs to pay an advance of at least Fr. 1'000.- , the amount of which varies according to the complexity of the case and the applications (amount of the maintenance contribution(s) and other measures) (art. 30 RTFMC).
If your resources are insufficient to ensure the defence of your interests, you can request legal aid.
Step 3: attending the hearing
The court summons you and your spouse to a conciliation hearing particularly in an attempt to reach an agreement on the effects of the divorce.
If there is no agreement on the effects of the divorce, the proceedings will continue and the court will give your spouse the opportunity to express his/her views in writing on your request.
If you are in dispute about residence of your minor child or children, or about visiting rights, the court may decide to request a report from the parental separation assessment and support Service (SEASP).
The court may appoint a deputy to represent the child (representative deputyship).
Step 4: receive the judgment
The judge's decision is communicated to you by mail, if necessary, through your counsel (lawyer, legal advice service).
What are the costs of a procedure?
The costs of proceedings include court fees (fees, costs of taking evidence, translation costs and costs of representing the child), which may be covered by an advance payment to cover all or part of the court costs, as well as legal costs. If a party instructs a lawyer, this will result in additional costs, separate from the court costs.
Below you will find the court costs for divorce by a unilateral application and divorce by joint application. Please note that these costs only relate to court fees and do not include other types of costs that may arise during the proceedings, such as interpreter fees or expert opinions requested by the court.
Depending on the course of the proceedings and the outcome of the dispute, the procedural costs set by the court may sometimes be lower or higher than the amounts defined in the règlement fixant le tarif des frais en matière civile (RTFMC).
For example :
- If an application has been declared inadmissible, the court may set costs lower than those indicated.
- If the advance payment is a certain amount, but publication in the Feuille d’Avis Officiel (FAO) is required, the final costs may be higher than the advance payment made.
More information concerning the costs of civil proceedings
Fees for divorce by a unilateral application in francs
This chart shows the breakdown of court fees (emoluments)
- At first instance (left)
- At second instance (right) in the event of an appeal against the decision
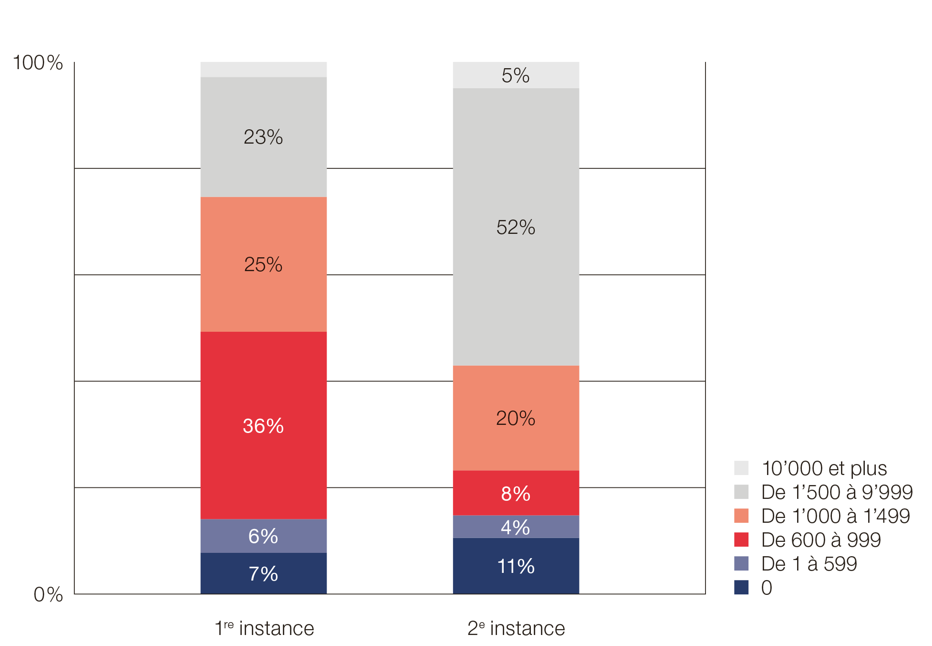
Please note: the fee for a divorce by a unilateral application is a minimum of CHF 1'000.-. However, it is common for the judge to be able to reconcile the parties during the hearing and help them reach an agreement. In such cases, the fees may be reduced (to less than the advance payment of CHF 1'000.-), which explains why the fees are less than CHF 1'000.- in nearly 50% of cases.
Fees for divorce by a joint application in francs
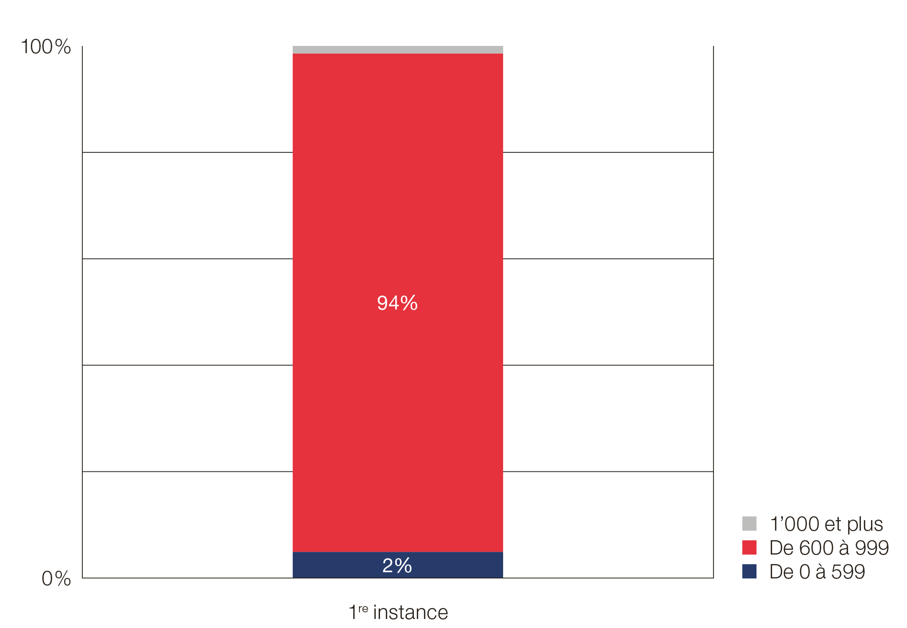
For a divorce by a joint application, which in almost all cases is finalised at first instance, the initial advance payment is CHF 600.-. In rare cases, the parties may not agree on all aspects of the procedure, which may result in additional costs.
Fees relating to measures for the protection of the marital union (MPUC) in francs
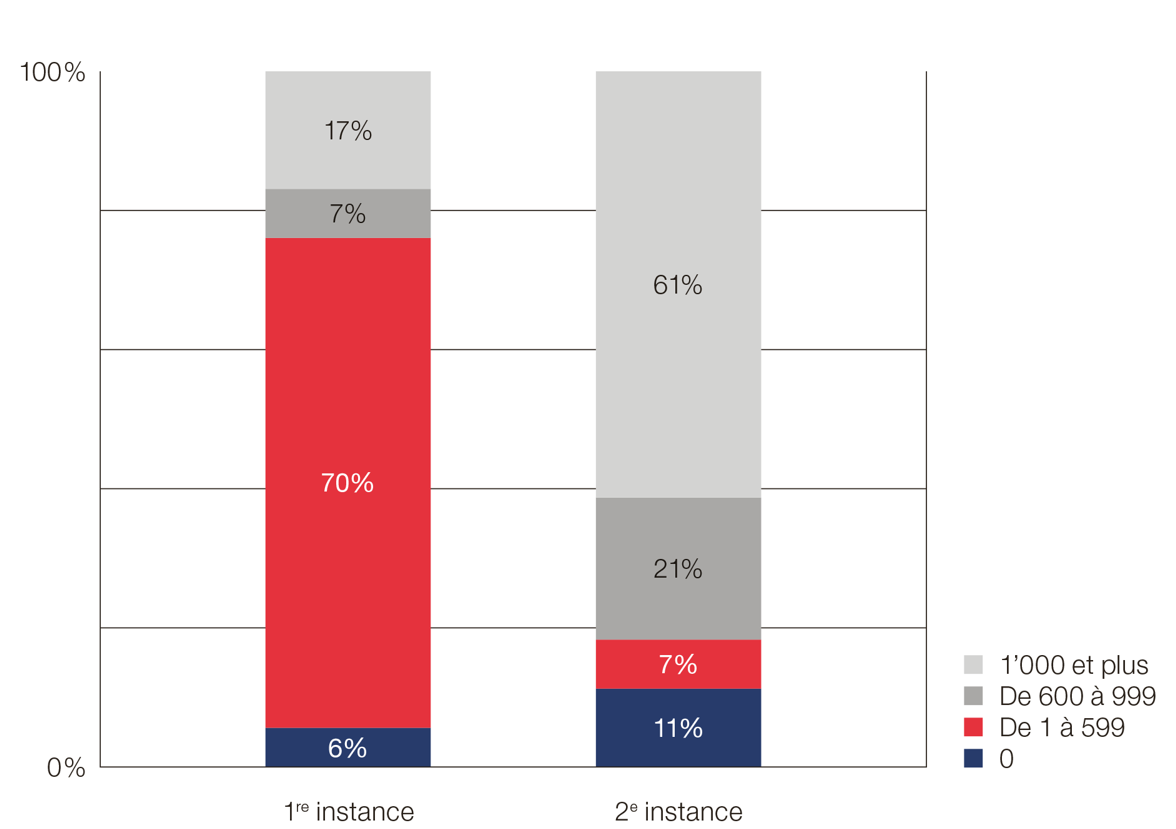
As far as the measures for the protection of the marital union are concerned (MPUC) article 31 RTFMC provides for a fixed fee for decisions ranging from CHF 150.- to CHF 5’000.-, depending on the complexity and scope of the case.
In practice:
- In the first instance, nearly 80% of proceedings result in fees of less than CHF 600.-.
- In the second instance, fees are generally higher than CHF 1’000.-.
In accordance with Article 98 paragraph 1 of the Code of Civil Procedure (CCP), the court may also require an advance payment of up to half of the estimated legal costs at the start of the proceedings.

How long does a proceeding take?
Duration of divorce proceedings based on a unilateral application
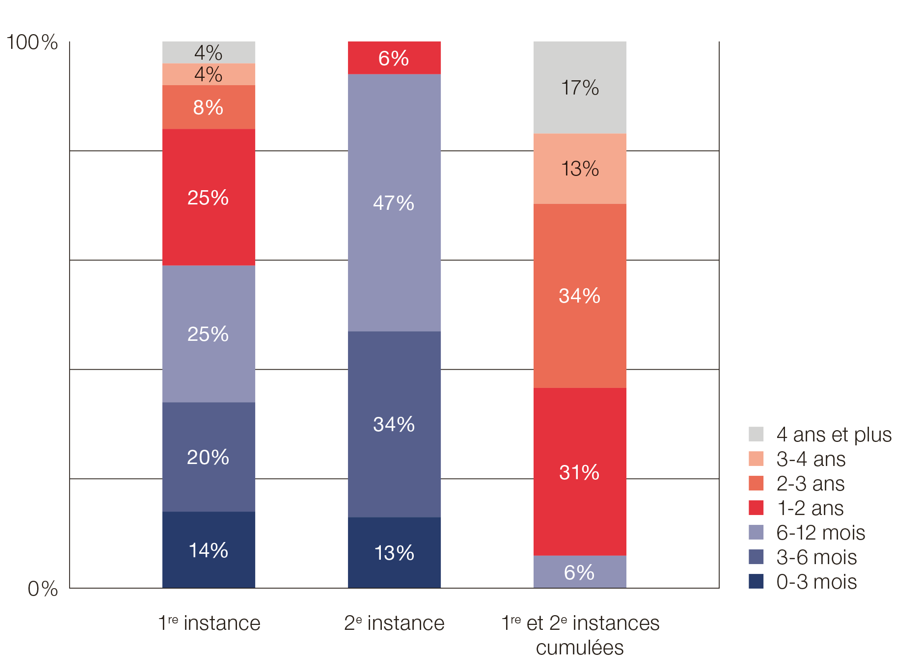
-
In the first instance, nearly 60% of proceedings are completed in less than a year and more than 80% are completed in less than two years.
-
In the second instance, more than 90% of proceedings are completed in less than a year.
Duration of a divorce proceeding by a joint application
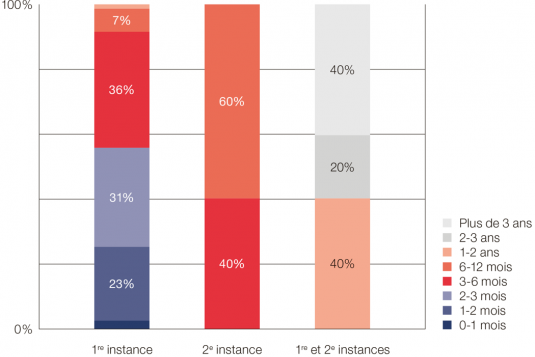
- In the first instance, more than 90% of divorce proceedings by a joint application are completed in less than six months.
- Given the nature of the proceeding, less than 1% of them are brought before a higher court.
Duration of measures for protection of the marital union (MPUC)

- At first instance, more than 85% of MPUC proceedings are completed within one year or less.
- At second instance, almost all proceedings are completed within less than one year.

Application forms
Divorce by joint request
To ask for a divorce, on the basis of an agreement between the two spouses.
The spouses can submit a total agreement (on all points) or partial (some points remain contentious and will be decided by the judge) to the court.
Practical guide
Request for precautionary measures during divorce proceedings
To request the urgent intervention of the judge during the divorce proceedings.
Request for measures for the protection of the marital union
To request the intervention of the judge when no divorce proceedings have been initiated (for example, to determine maintenance contributions, custody and visitation rights over the children, the allocation of the house to one of the spouses, etc.).
Contacts
Address
Contact details
Desk
Opening hours
9h-12h / 13h30-16h00
Filing applications of ex-parte interim measures and seizures to the Tribunal de première instance
Urgent requests must be submitted no later than the closure of the desk at 4:00 pm.
In the event of filing with the greffe universel of the Judiciary power, urgent applications will generally be processed in the 24 hours following payment of the fee and therefore, in principle, the following day, particularly for documents filed in the afternoon.
Mailing address
Tribunal de première instance
Case postale 3736
1211 Genève 3
Questions/answers
You can bring a case to the Tribunal de première instance of Geneva if you or/and your spouse are domiciled in Geneva.
No, you are not obliged. However, it is highly recommended, especially if you have a disagreement with your spouse and the case is complex.
You can access the list of lawyers and legal advice services in Geneva.
The court decides, depending on the case, whether the children are heard in person.
At the end of the last hearing, the court may ask you to choose between 2 types of decisions:
- A judgment without the grounds: the decision will include only the conclusions, i.e. the solution of the dispute.
- A judgment stating the grounds: the document will present the reasons that led the judge to render his/her decision.
A judgment stating the grounds is more expensive than a decision without grounds.